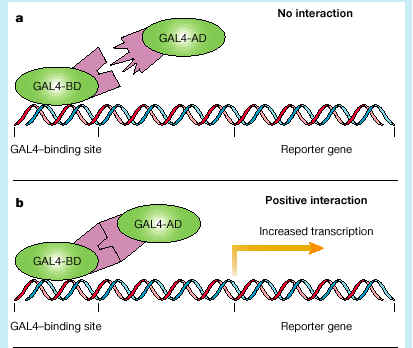
A yeast two hybrid assay is a protein-protein interation assay to determine if two proteins are interacting.
This works by having a "bait" protein that is tied to half of a well known protein like GAL4 that is tied to a reporter promoter. The "prey" protein then, if it interacts with the "bait" will bring the other half of the GAL4 protein together so that it can sit down on the promoter and activate transcruption of the reporter gene.
Thus, if transcription of the reporter takes place, the two proteins "bait" and "prey" are interacting.
Most common reporter genes used are lacZ, leu2, Ade1 and Mel2. LacZ and Mel2 are used in beta-Gal and alpha Gal assays wherein the interaction can be quantified by a change in colour. Ade1 and Mel2 are nutritional reporters wherein the yeast can grow in the absence of Adenine and Leucine in the media as they can make their own.
Alternatively, one can use a Yeast-Three hybrid approach in order to identify or validate targets of small molecules. If a small molecule mediates the interation of bait and prey , the reporter genes downstream of the Gal promoter are turned on.