Rosalind Frankling was a biophysicist who made significant, although not properly recognized, contributions to the discovery of the structure of DNA while working at King's College in Cambridge. Franklin is best known for her work on X-ray crystallography, which lead to several important diffraction pictur

Rosalind Franklin at King's College
es including the famous photo 51. This photo was the first evidence of DNA's
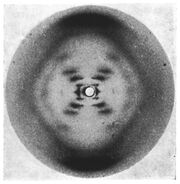
Franklin's famous photo 51. Diffraction image of the double helix.
helix shape, and it was a critical piece of information for Watson and Crick's 1953 model. Rosalind Franklin was the first to acknowleged the two forms of DNA molecule (Type A and B), as well as to hypothesize that the phosphate backbone is outside of the helix. Her work was published third in the series of DNA Nature articles in which she described the structure of Type B DNA molecule, but was overshadowed by Watson and Crick's first publication on the structure of DNA. After leaving King's college, Rosalind Franklin shifted her work to do research and signficant contributions on the tobacco mosaic virus and the polio virus. Franklin died of cancer in 1958 from ovarian cancer.